2 Degrees C To F
candidatos
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
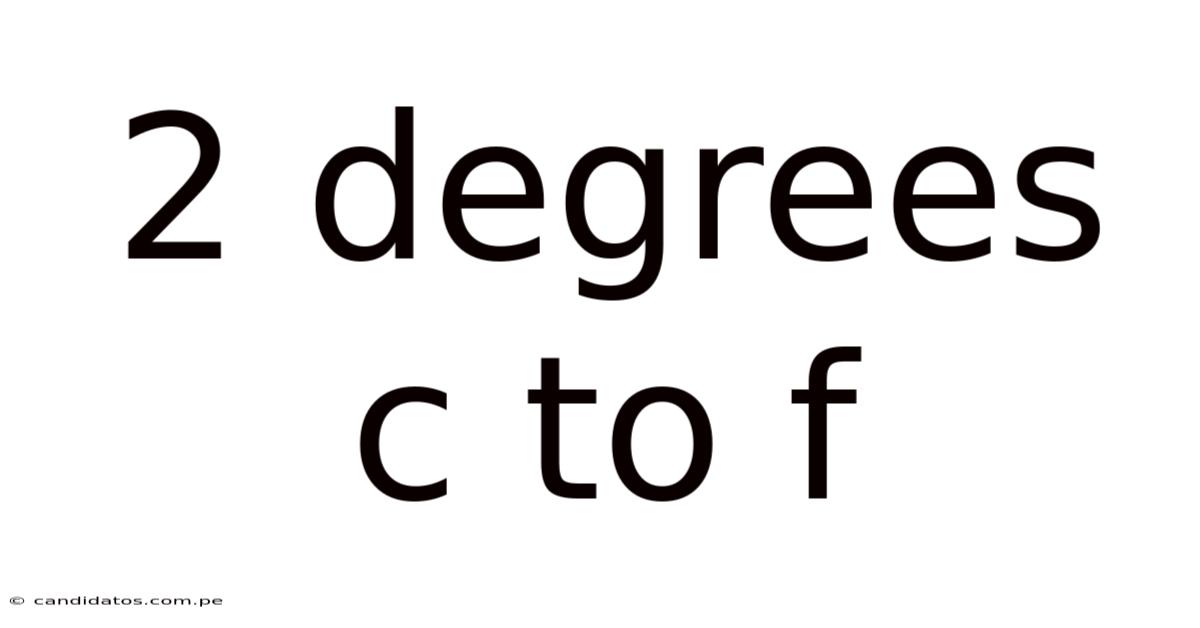
Table of Contents
Converting 2 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various fields, from cooking and everyday life to scientific research and engineering. This article provides a thorough explanation of how to convert 2 degrees Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F), exploring the underlying formula, practical applications, and addressing frequently asked questions. We'll delve into the history of these temperature scales and offer a deeper understanding of their relationship, making this conversion a breeze for everyone, regardless of their scientific background.
Introduction: Celsius and Fahrenheit – A Brief History
The two most commonly used temperature scales globally are Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F). While Celsius, also known as the centigrade scale, is the standard unit for most of the world, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in the United States and a few other countries. Understanding the differences and how to convert between them is vital for seamless communication and accurate data interpretation.
Celsius is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, set at 0°C and 100°C respectively, at standard atmospheric pressure. Fahrenheit, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, has a more complex history. Its zero point was originally based on a brine solution's freezing point, and the scale's upper and lower points were initially set according to human body temperature and a winter's day in his location. This resulted in somewhat arbitrary points, making the Celsius scale more intuitively understandable.
The Conversion Formula: From Celsius to Fahrenheit
The core of converting Celsius to Fahrenheit lies in a simple yet powerful formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula dictates that to convert a Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit, you multiply the Celsius value by 9/5 (or 1.8) and then add 32. Let's apply this to our specific case: converting 2°C to °F.
- Step 1: Multiplication: 2°C × 9/5 = 3.6°
- Step 2: Addition: 3.6° + 32° = 35.6°F
Therefore, 2 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 35.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Converting 2°C to °F
For clarity, let's break down the conversion process into easily manageable steps:
- Identify the Celsius Temperature: Our starting point is 2°C.
- Multiply by 9/5: Multiply the Celsius temperature (2) by the fraction 9/5. This step accounts for the difference in the scale's increments. 2 * 9/5 = 3.6.
- Add 32: Add 32 to the result obtained in step 2. This is because the zero points of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are different. 3.6 + 32 = 35.6.
- State the Fahrenheit Equivalent: The final answer is 35.6°F. This means that a temperature of 2°C is the same as a temperature of 35.6°F.
Practical Applications of Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- International Communication: Facilitates clear communication about weather, cooking temperatures, and industrial processes between individuals and organizations in different regions.
- Scientific Research: Enables accurate data comparison and analysis across studies conducted using different temperature scales.
- Engineering and Manufacturing: Ensures precise control of temperature in industrial processes, preventing errors and optimizing efficiency.
- Medicine: Accurate temperature conversions are crucial in medical diagnostics and treatment, ensuring patient safety.
- Meteorology: Accurate temperature reporting is essential for weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
Understanding the Mathematical Basis of the Conversion Formula
The conversion formula (°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32) is derived from the relationship between the boiling and freezing points of water on both scales. The difference between the boiling and freezing points of water in Celsius is 100°C (100 - 0 = 100), while in Fahrenheit, it's 180°F (212 - 32 = 180). The ratio of these differences (180/100) simplifies to 9/5, which forms the basis of the multiplication factor in the formula. The addition of 32 adjusts for the difference in the zero points of the two scales.
This mathematical relationship ensures a precise conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit, ensuring consistency and accuracy in any application.
Beyond 2°C: Converting Other Celsius Temperatures
The formula presented above applies universally for any Celsius temperature conversion to Fahrenheit. Simply substitute the Celsius value into the formula to obtain the corresponding Fahrenheit value.
For example:
- 10°C to °F: (10 × 9/5) + 32 = 50°F
- -10°C to °F: (-10 × 9/5) + 32 = 14°F
- 0°C to °F: (0 × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
- 100°C to °F: (100 × 9/5) + 32 = 212°F
This demonstrates the versatility and broad applicability of the formula.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A1: Historically, different scales developed independently. Celsius emerged as a more logically structured system based on water's properties, while Fahrenheit, with its more arbitrary points, predates it and remains in use due to historical reasons and inertia.
Q2: Which scale is more accurate?
A2: Both scales are equally accurate in measuring temperature. The difference lies in their units and reference points, not their precision.
Q3: Can I use an online converter instead of the formula?
A3: Yes, many online converters are readily available for quick and easy Celsius to Fahrenheit conversions. However, understanding the formula empowers you with a deeper understanding and allows for conversions even without internet access.
Q4: Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius and Fahrenheit?
A4: Yes, other temperature scales exist, such as Kelvin (K), which is the absolute temperature scale used extensively in scientific research. The Kelvin scale begins at absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases.
Q5: What is the significance of 32 in the conversion formula?
A5: The 32 in the formula accounts for the difference in the zero points of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. The freezing point of water is 0°C and 32°F, hence the addition of 32 adjusts for this offset.
Conclusion: Mastering the Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
Converting 2°C to 35.6°F, as demonstrated above, is a straightforward process once the conversion formula is understood. This seemingly simple conversion has far-reaching implications in various fields. By understanding both the practical application and the underlying mathematical principles, one can confidently navigate temperature conversions and appreciate the importance of standardized measurement systems in facilitating clear communication and accurate data interpretation across diverse disciplines. This knowledge empowers you to tackle any temperature conversion task with accuracy and confidence. Remember, the key is to master the formula and understand its derivation – then you'll be well equipped to handle any temperature conversion challenge that comes your way.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Colors That Start With S
Sep 24, 2025
-
Describing Words Beginning With G
Sep 24, 2025
-
Item Of Furniture Crossword Clue
Sep 24, 2025
-
How Much Is A Litre
Sep 24, 2025
-
Yellow Leaves On Rose Plants
Sep 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 Degrees C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.